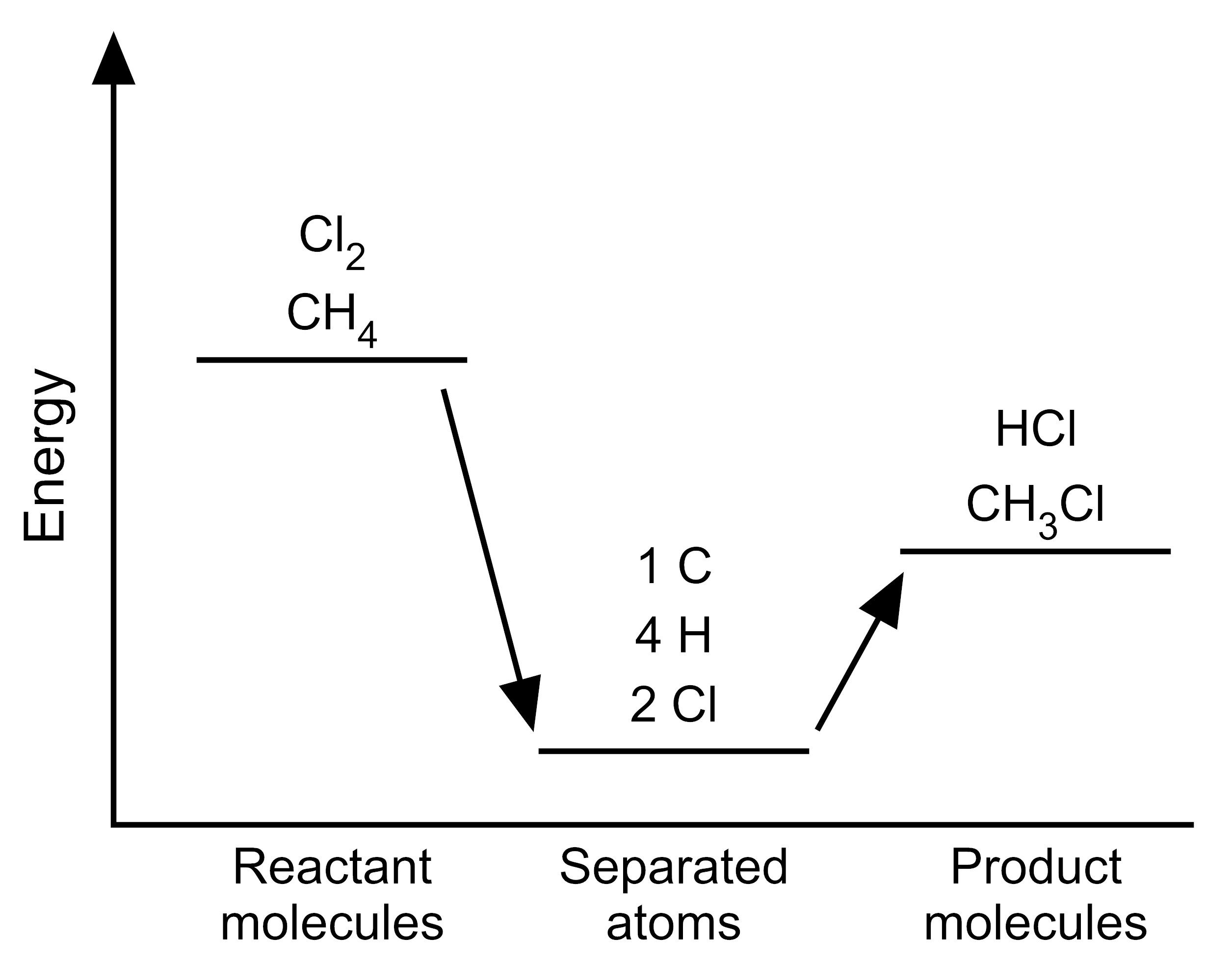
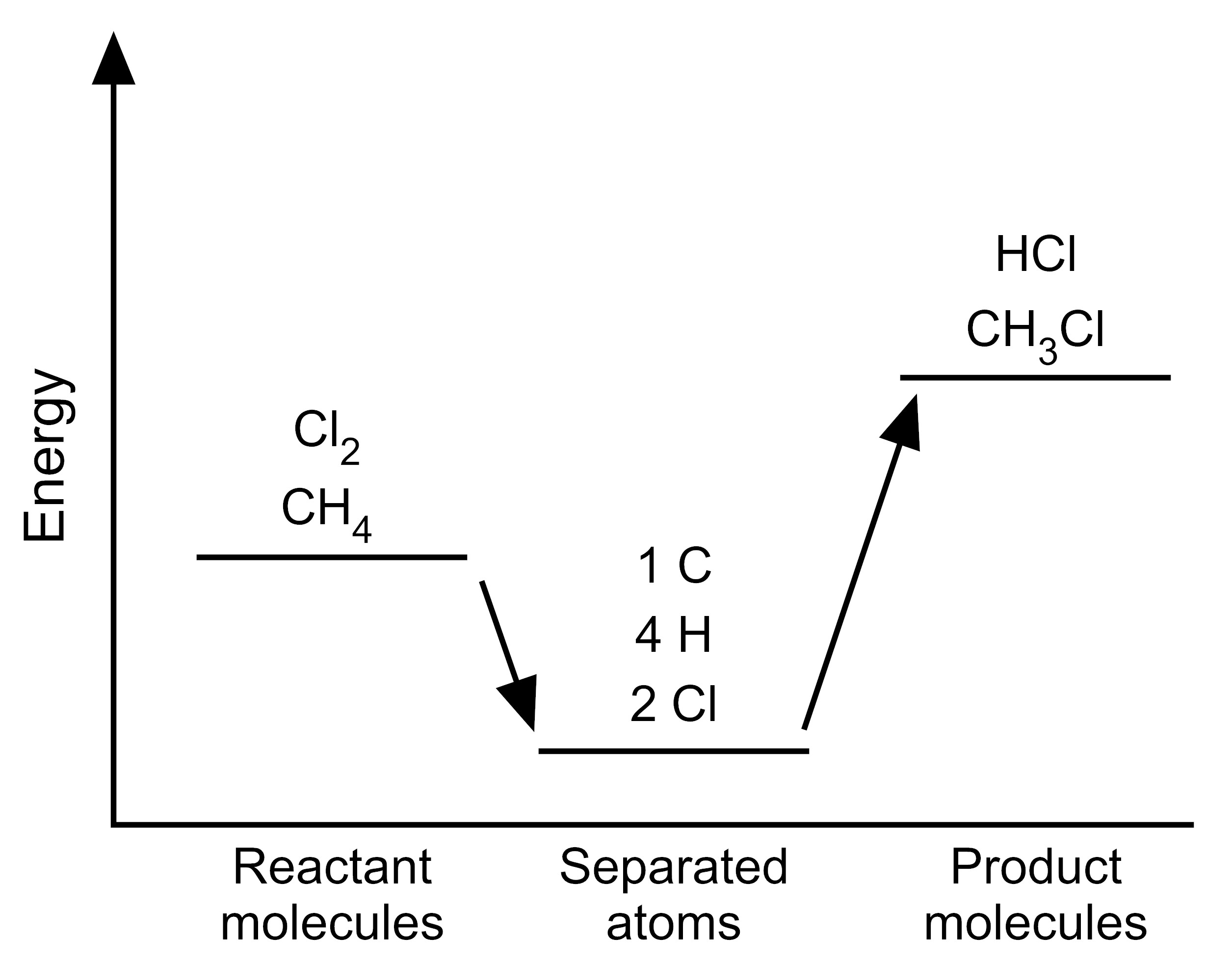
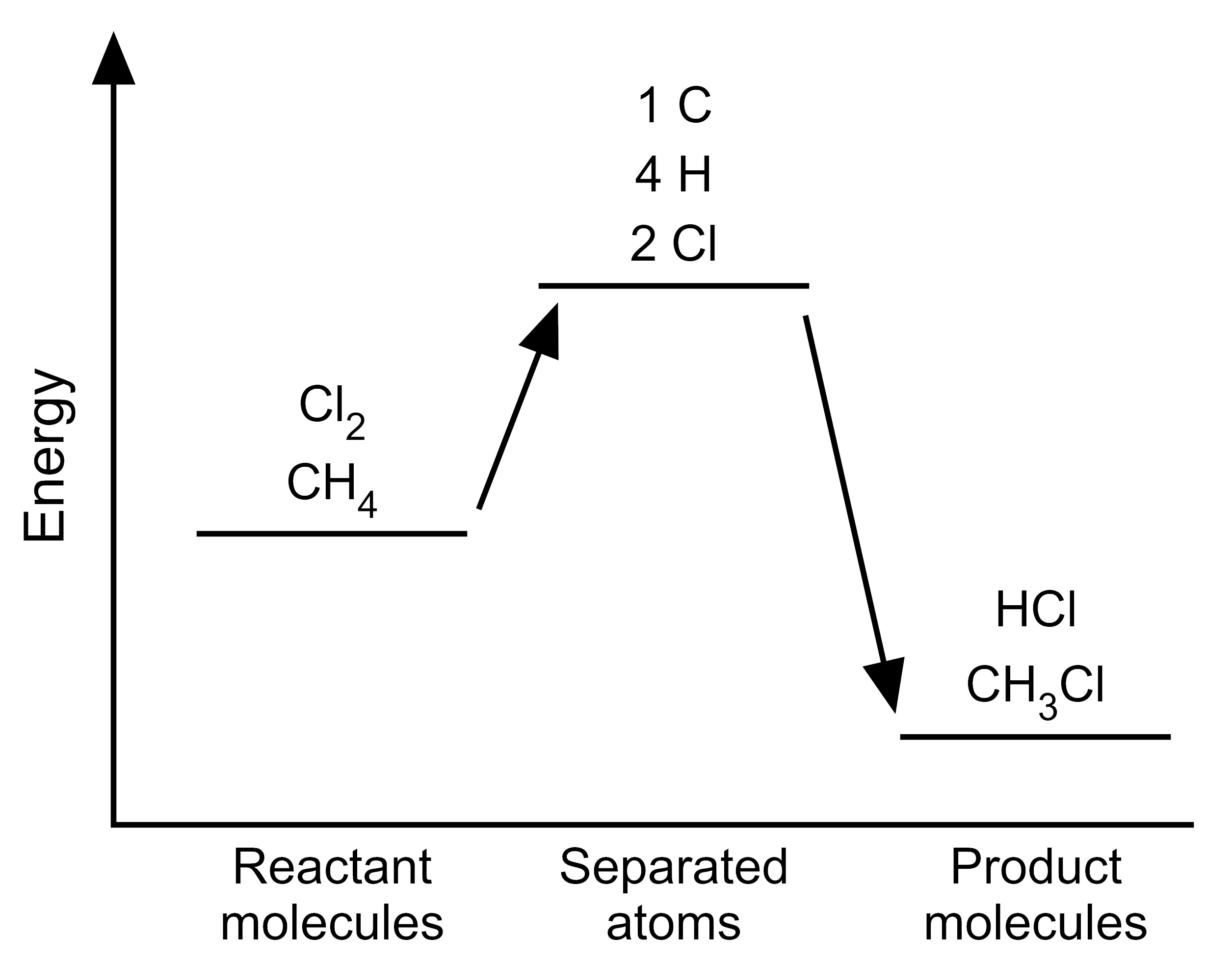
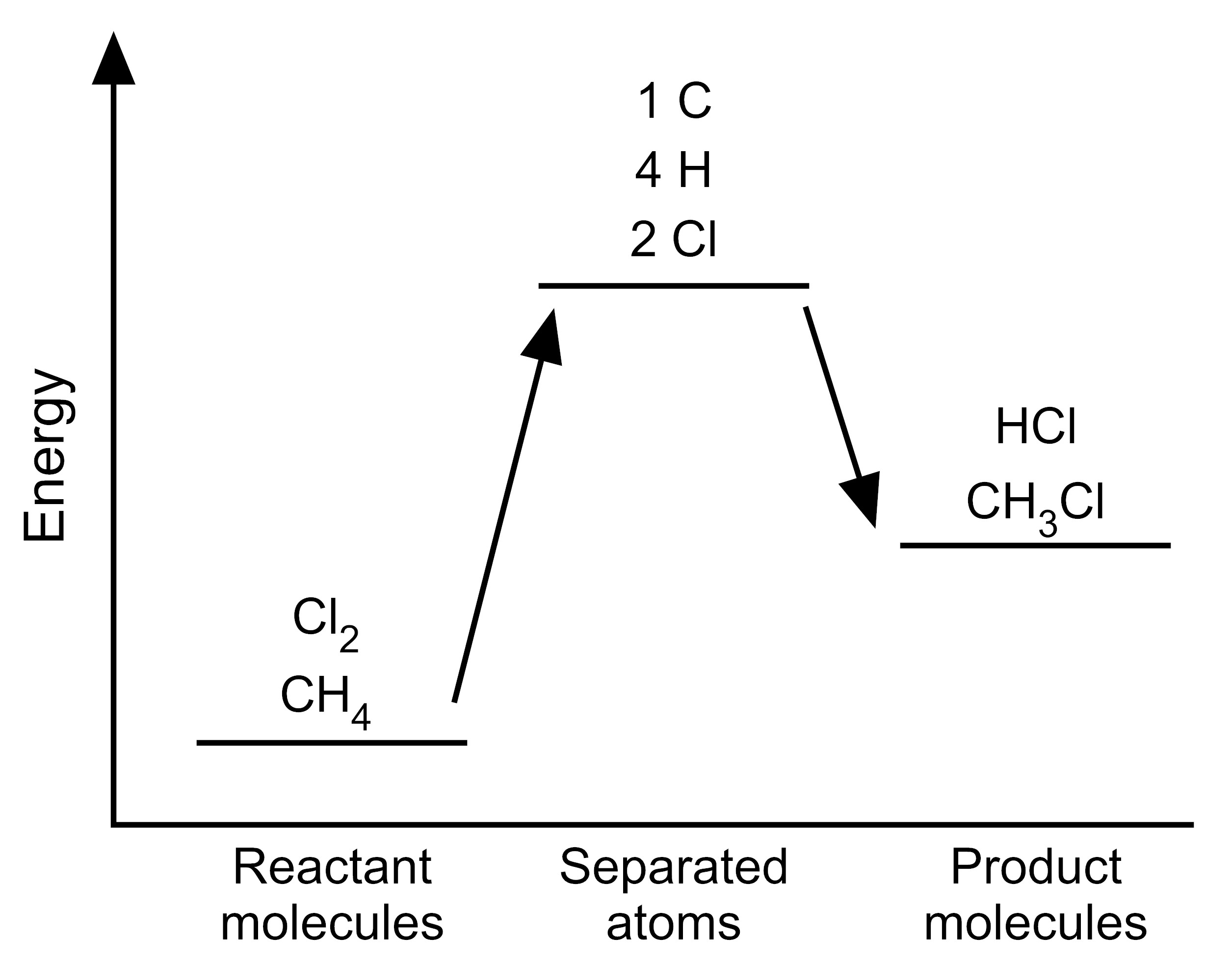
Item EB054002: The reaction between methane and chlorine takes in energy because the total bond energy of the reactants is greater than the total bond energy of the products. (This item uses graphs.)
One mole of methane molecules (CH4) reacts with one mole of chlorine molecules (Cl2) to form one mole of chloromethane molecules (CH3Cl) and one mole of hydrogen chloride molecules (HCl) (A mole is a very large quantity of molecules). The equation for this chemical reaction is shown below.
CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl
Scientists have determined the amount of energy associated with breaking and forming the bonds between the atoms that make up the molecules of CH4, Cl2, CH3Cl, and HCl. We can use these bond energies to predict whether this reaction will release energy or take in energy. The table below show the total bond energy of one mole of CH4 plus one mole of Cl2 and the total bond energy of one mole of CH3Cl plus one mole of HCl. [A kilojoule (kJ) is a unit of energy.]
| Total bond energies in kilojoules (kJ) | ||
| Reactants | CH4 + Cl2 | 624 kJ |
| Products | CH3Cl + HCl | 763 kJ |
Based on this information, which model represents the energy changes that occur during this reaction?
- Distribution of Responses

- Points Earned
| Group | Correct | Total | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 35 | 164 | 21% |
| Grades | |||
| 6–8 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 9–12 | 28 | 141 | 20% |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 18 | 83 | 22% |
| Female | 11 | 62 | 18% |
| Primary Language | |||
| English | 27 | 129 | 21% |
| Other | 1 | 9 | 11% |
- Distribution of Responses

- Points Earned
| Group | Correct | Total | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 37 | 177 | 21% |
| Grades | |||
| 6–8 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 9–12 | 34 | 164 | 21% |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 15 | 89 | 17% |
| Female | 20 | 72 | 28% |
| Primary Language | |||
| English | 30 | 151 | 20% |
| Other | 3 | 11 | 27% |
- Disciplinary Core Ideas
- PS1.A A stable molecule has less energy than the same set of atoms separated; one must provide at least this energy in order to take the molecule apart.
PS1.B Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.