Item NG069005: In a situation involving two slides, and assuming no energy transfer between the slides and the students sliding on them or between the students and the air around them, two students of the same mass sliding down differently shaped slides will have the same speed at the bottom of the slides because the only source of motion energy is the change in gravitational potential energy, and both students experience the same change in gravitational potential energy.
Imagine two slides that are shaped differently but start and end at the same height above the ground as shown below. Two students slide down from the top of the two different slides starting from rest. The students weigh the same.
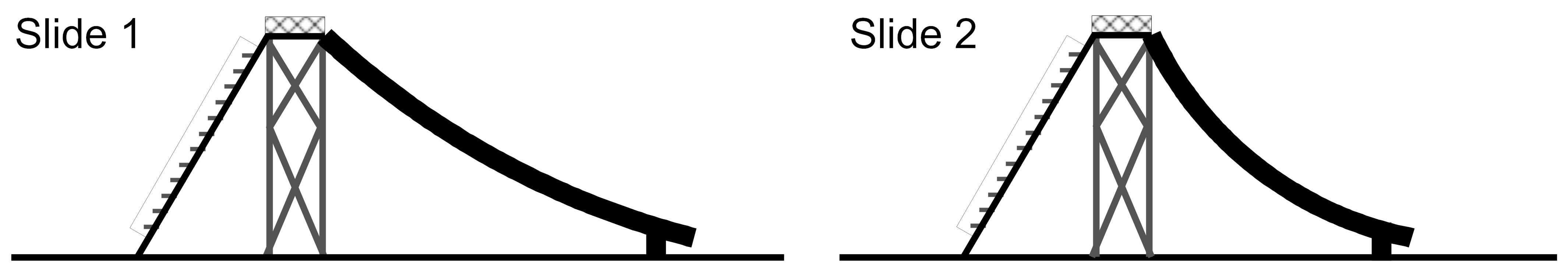
Which student has the greater speed at the bottom of the slide and why? (Assume no energy is transferred between the students and the slides or between the students and the air around them.)
- The student on Slide 1 because that student traveled a longer distance, so there was more time for new energy in the form of kinetic energy (motion energy) to be made
- The student on Slide 2 because that student initially encountered a steeper slope, so more new energy in the form of kinetic energy (motion energy) was made
- The student on Slide 2 because that student traveled a shorter distance and did not lose as much kinetic energy (motion energy) or gravitational potential energy as the student on Slide 1
- The students have the same speed because the only source of kinetic energy (motion energy) is the change in gravitational potential energy, and both students experienced the same change in gravitational potential energy.
Answer Choice |
Overall |
Grades |
Gender |
Primary Language |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 2861 |
4–5 n = 0 | 6–8 n = 1457 |
9–12 n = 1404 |
Male n = 1301 |
Female n = 1491 |
English n = 2589 |
Other n = 191 |
||
| A. | The student on Slide 1 because that student traveled a longer distance, so there was more time for new energy in the form of kinetic energy (motion energy) to be made | 14% | N/A | 17% | 12% | 15% | 14% | 14% | 20% |
| B. | The student on Slide 2 because that student initially encountered a steeper slope, so more new energy in the form of kinetic energy (motion energy) was made | 51% | N/A | 51% | 52% | 49% | 53% | 52% | 41% |
| C. | The student on Slide 2 because that student traveled a shorter distance and did not lose as much kinetic energy (motion energy) or gravitational potential energy as the student on Slide 1 | 22% | N/A | 22% | 22% | 22% | 22% | 22% | 25% |
| D. | The students have the same speed because the only source of kinetic energy (motion energy) is the change in gravitational potential energy, and both students experienced the same change in gravitational potential energy. | 12% | N/A | 10% | 14% | 14% | 10% | 12% | 14% |

