Item RG199001: During rusting, the substances have less chemical energy after the reaction because some energy was transferred out of the system.
During science class, a student places a piece of steel wool in a flask and seals the flask with a balloon. She notices that the steel wool starts to react with the oxygen in the flask. When she picks up the flask, she also notices that the flask feels warm.
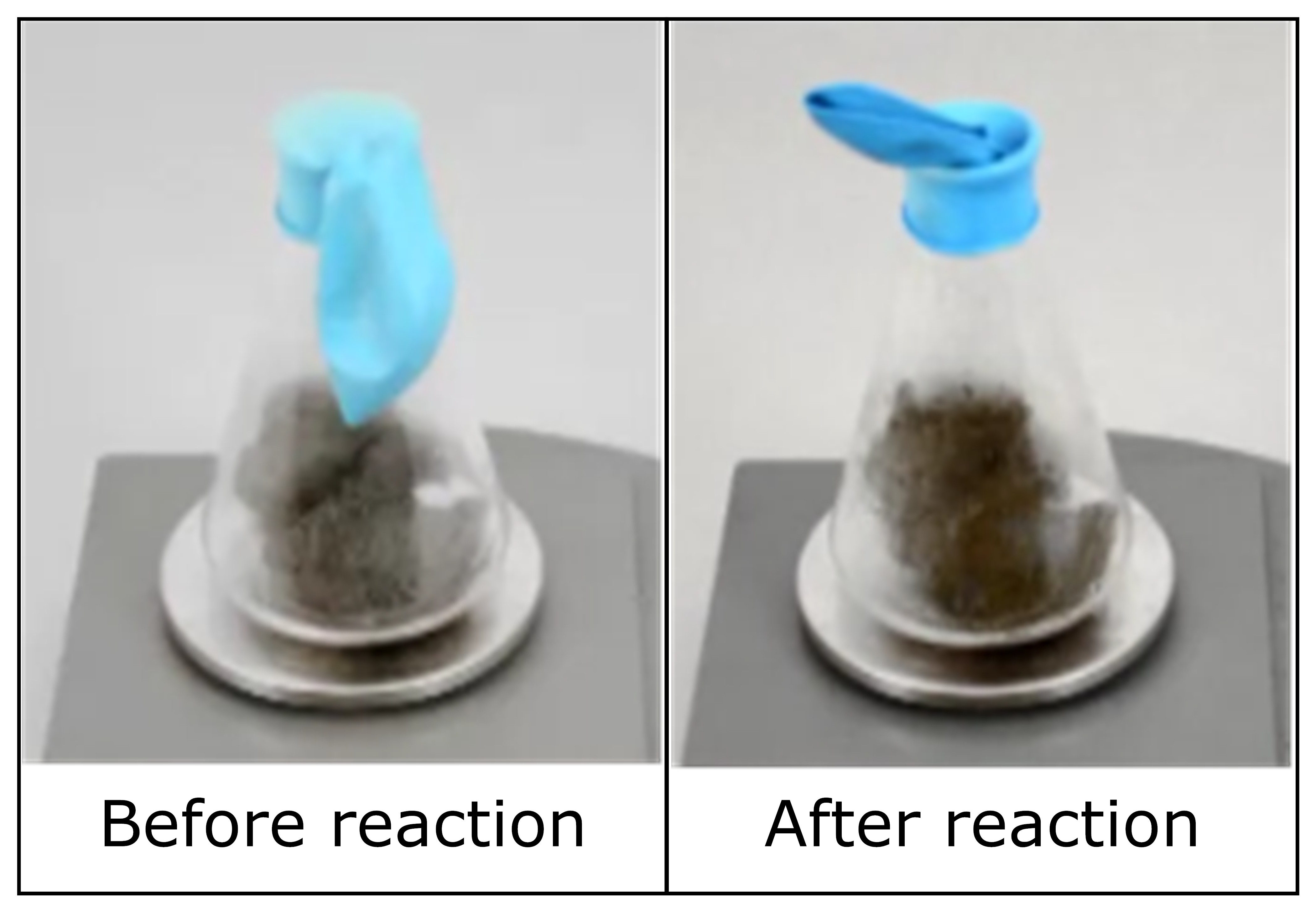
After the chemical reaction takes place inside the flask, do the substances inside the flask have more, less, or the same amount of chemical energy as before the reaction? Why?
- The substances have more chemical energy after the reaction because the flask feels warmer.
- The substances have less chemical energy after the reaction because some of its energy was transferred out of the system.
- The substances have the same amount of chemical energy after the reaction. Even though the flask feels warmer, that does not change the amount of chemical energy the system has.
- The substances have the same amount of chemical energy after the reaction. The flask feels warmer because coldness was transferred from the flask to the surroundings.
- Distribution of Responses

- Scale Score for Item Difficulty
(200[Easy]-800[Difficult]) - 526
- Students Responding Correctly
| Group | Correct | Total | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 933 | 3244 | 29% |
| Grades | |||
| 4–5 | 36 | 190 | 19% |
| 6–8 | 477 | 1698 | 28% |
| 9–12 | 420 | 1356 | 31% |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 460 | 1518 | 30% |
| Female | 454 | 1665 | 27% |
| Primary Language | |||
| English | 856 | 2943 | 29% |
| Other | 60 | 234 | 26% |
- Disciplinary Core Ideas
- PS1.B Some chemical reactions release energy, others store energy.

