Item IE019015: Changes in a population (fish in a pond) may affect populations that are not directly connected by a feeding relationship (insects) even if they are several steps away in a food web.
The diagram below shows the feeding relationships between populations of plants and animals in and around a pond. The arrows point from the organisms being eaten to the organisms that eat them.
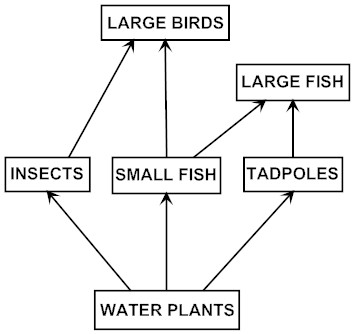
More people than usual go fishing and take a lot of the large fish out of the pond. Using only the relationships between the plants and animals shown in the diagram, what is likely to happen to the number of insects and why?
- The number of insects is likely to decrease because with fewer large fish to eat the tadpoles, there would be more tadpoles eating more water plants and fewer water plants available for the insects.
- The number of insects is likely to decrease because with fewer large fish for the large birds to eat, the large birds would have to eat more insects.
- The number of insects is not likely to change because large fish are not connected by an arrow in the diagram.
- The number of insects is not likely to change because people took only large fish out of the pond.
Answer Choice |
Overall |
Grades |
Gender |
Primary Language |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 1410 |
6–8 n = 756 |
9–12 n = 648 |
Male n = 675 |
Female n = 701 |
English n = 1204 |
Other n = 168 |
||
| A. | The number of insects is likely to decrease because with fewer large fish to eat the tadpoles, there would be more tadpoles eating more water plants and fewer water plants available for the insects. | 37% | 35% | 40% | 40% | 36% | 37% | 35% |
| B. | The number of insects is likely to decrease because with fewer large fish for the large birds to eat, the large birds would have to eat more insects. | 17% | 17% | 17% | 15% | 19% | 18% | 17% |
| C. | The number of insects is not likely to change because large fish are not connected by an arrow in the diagram. | 31% | 32% | 29% | 30% | 31% | 30% | 33% |
| D. | The number of insects is not likely to change because people took only large fish out of the pond. | 15% | 16% | 14% | 15% | 15% | 15% | 16% |

